CARYOPHYLLACEAE: PINK FAMILY
---
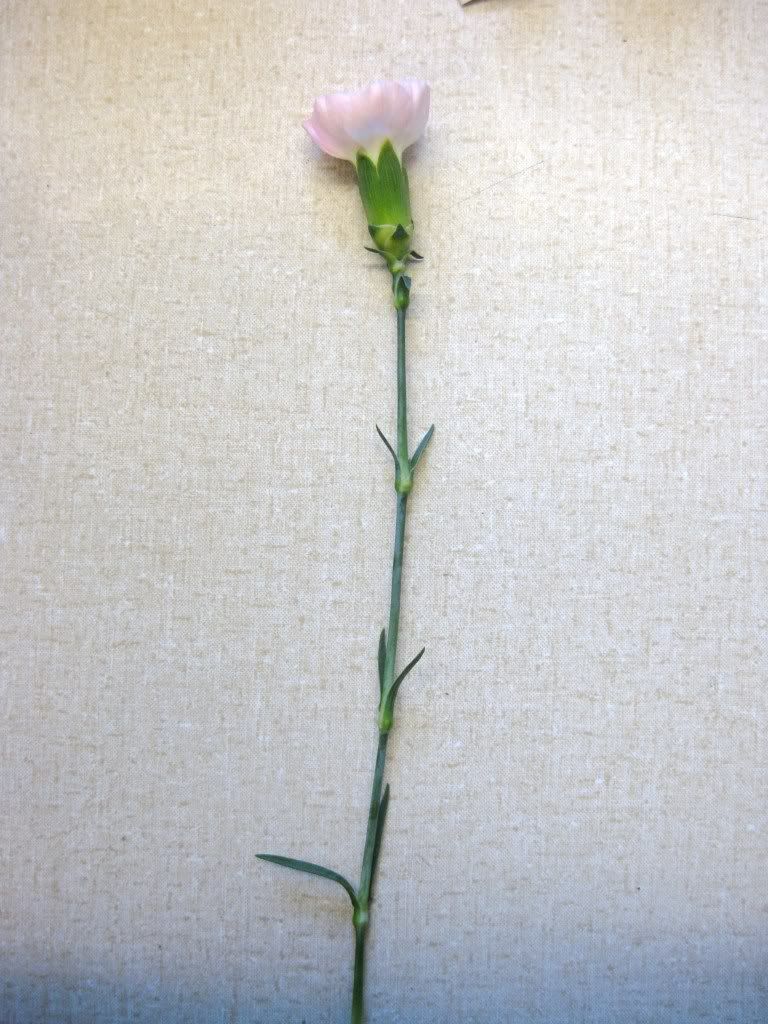
The flower and stem of the Carnations (Dianthus sp.). Note the opposite leaves and swollen nodes which are characteristic of the Pink family. Also, the inflorescence in this particular example is 'solitary'.
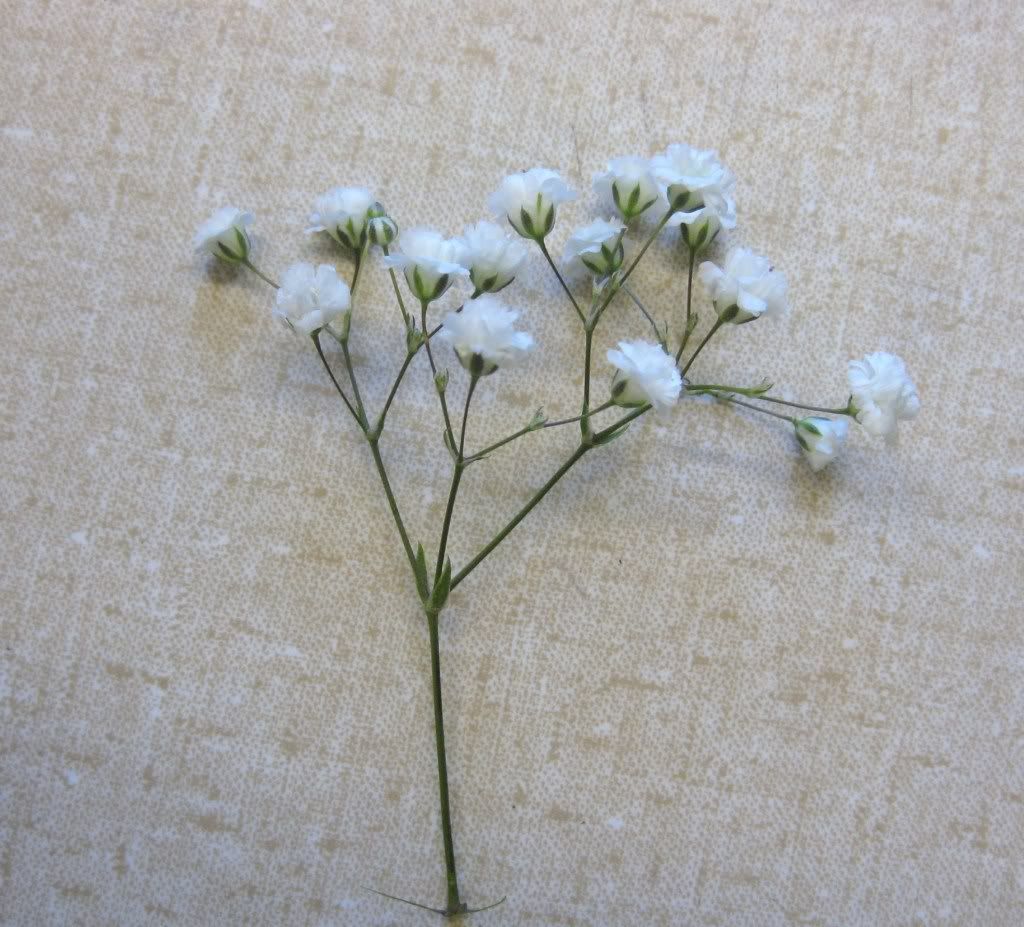
Flowers of some Gypsophila sp. flowers. What's the inflorescence here?
This is a cyme; the middle flower is the oldest/most mature.
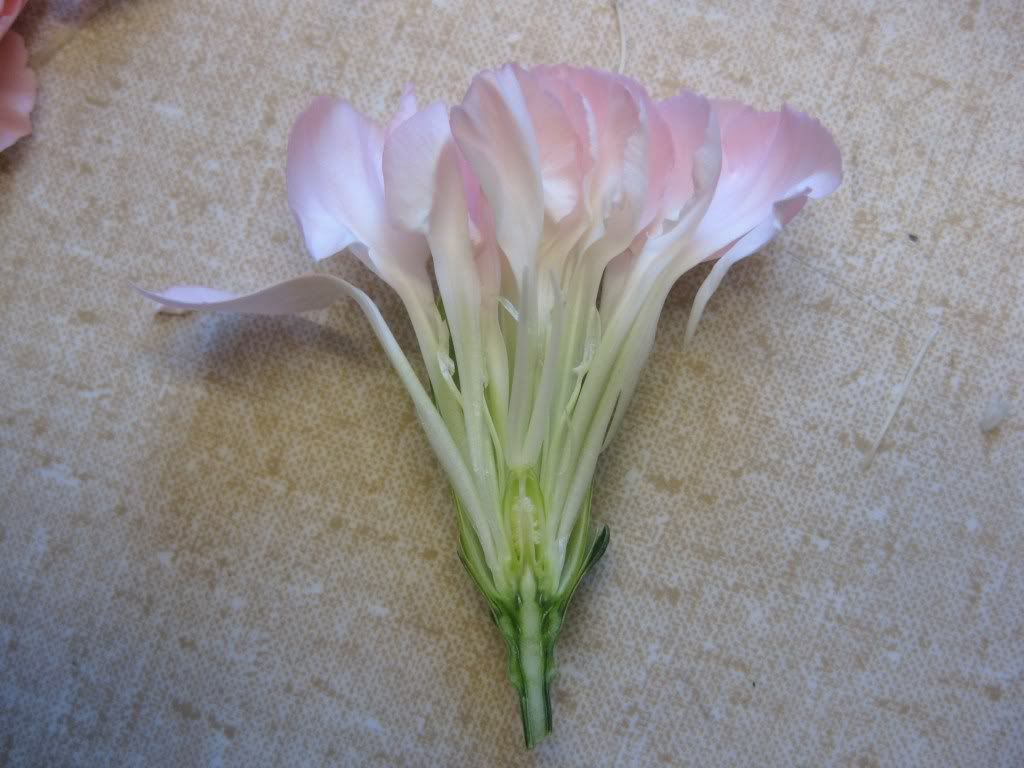
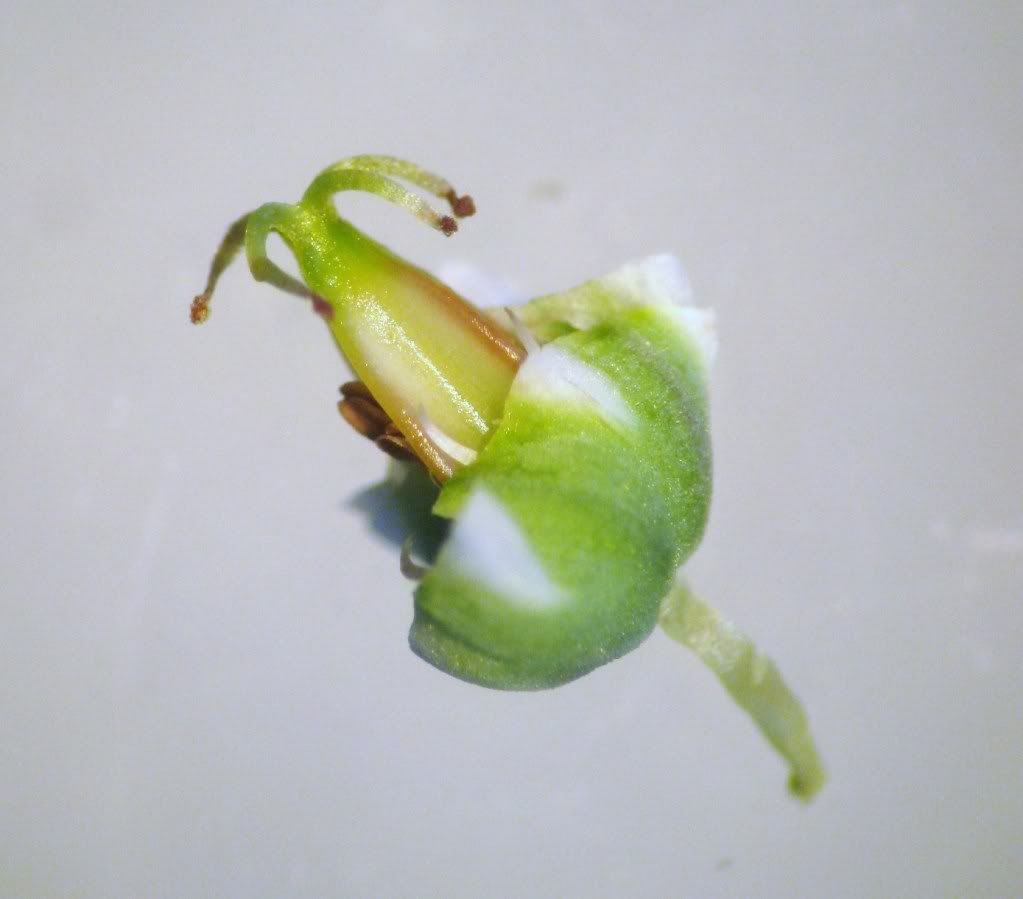
Back to the flower of the Carnations. Can you label the following structures? Sepals, petals, pistil, style, stigma, and stamen.
The white forking structure is the stigmatic surface. Why do we sometimes use 'stigmatic surface' instead of 'stigma'?
Two petals from the Carnations. The narrow basal portions are the claws.
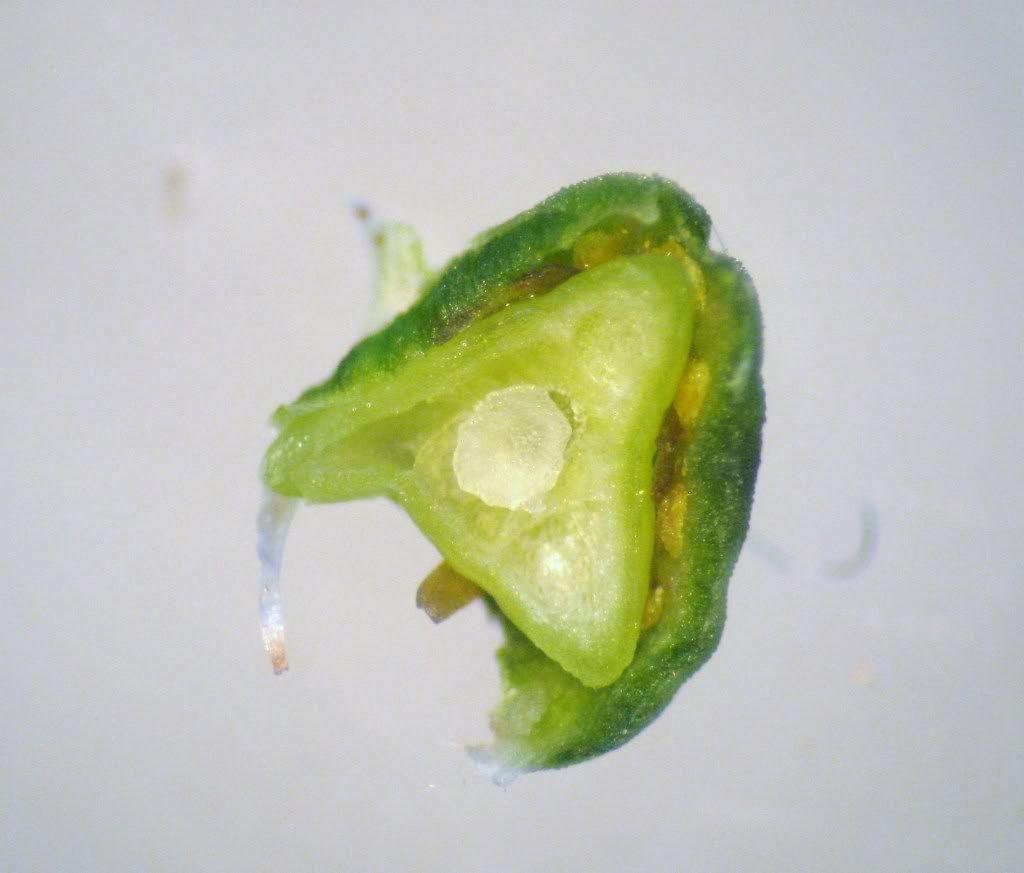
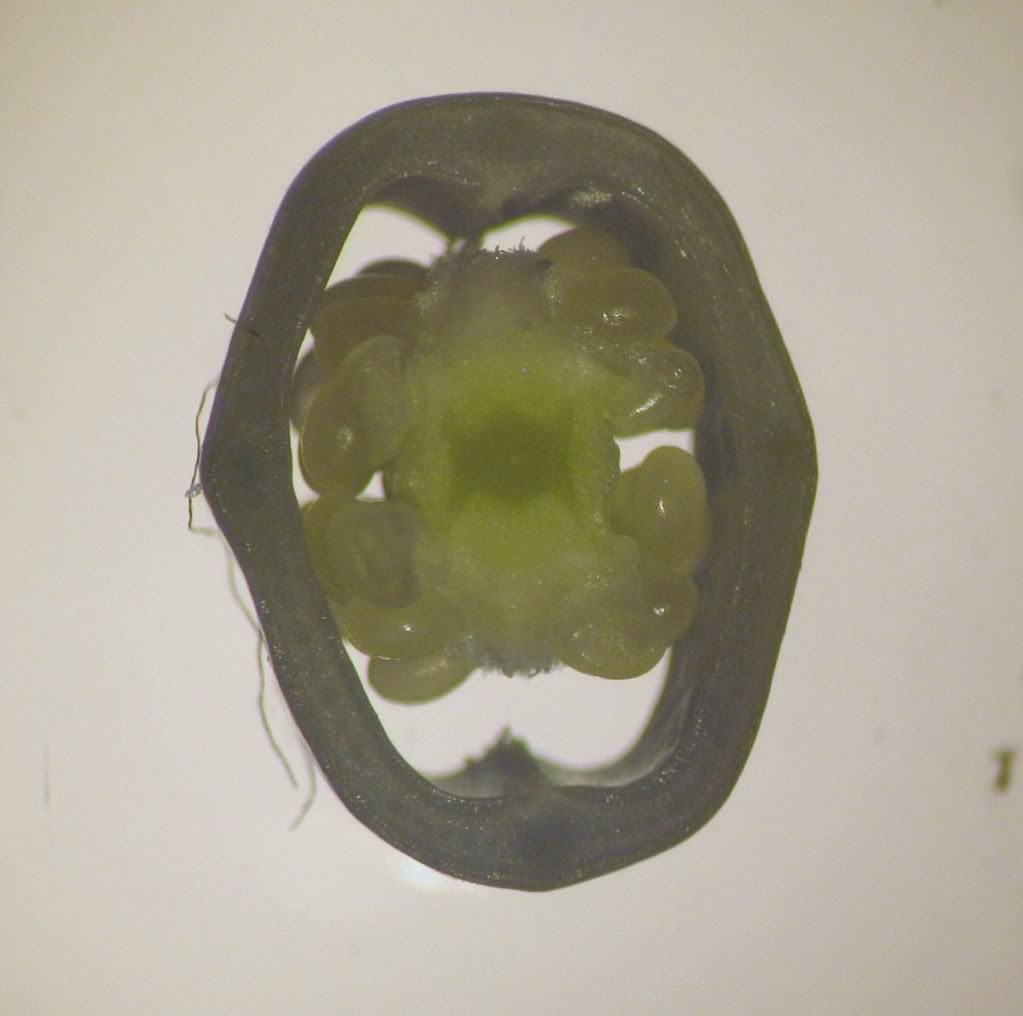
Cross-section of the Carnation ovary. The ovules are attached to a central column that arised from the base of the ovary and is not connected to the ovary wall. What is this kind of placentation called?
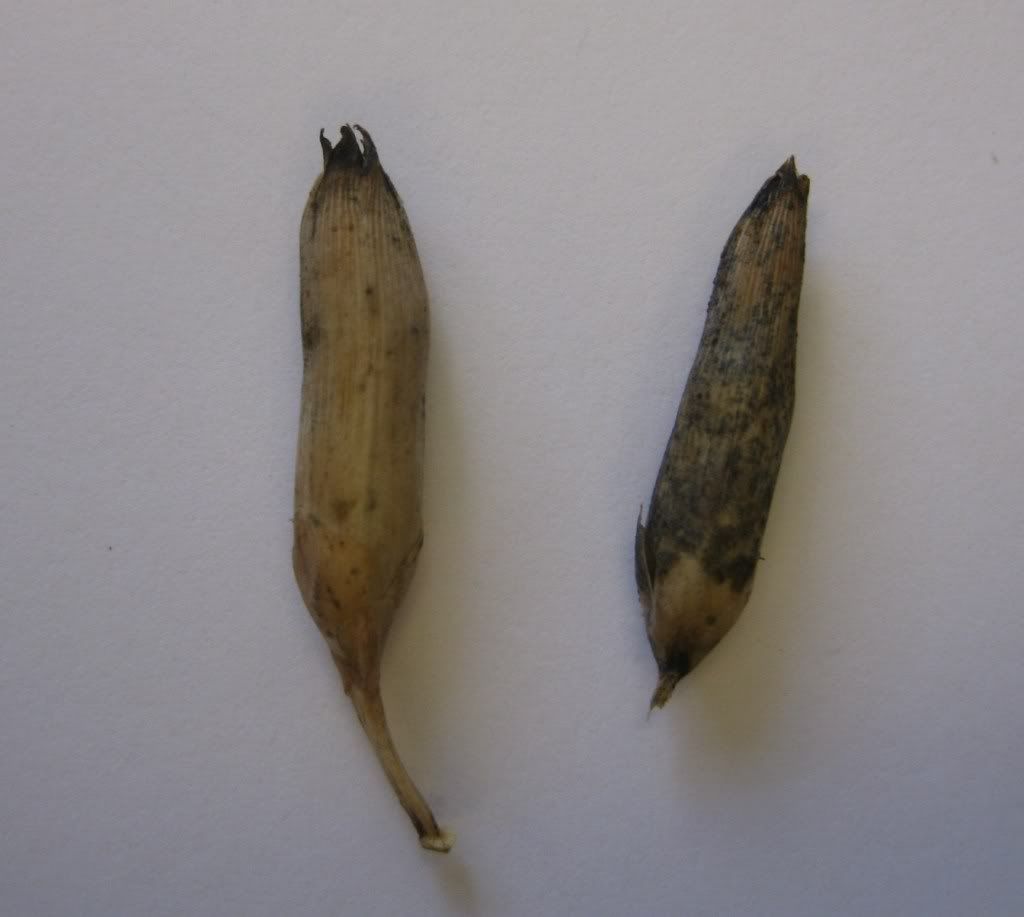
Two capsules from the Caryophyllaceae.
POLYGONACEAE - Buckwheat family
---
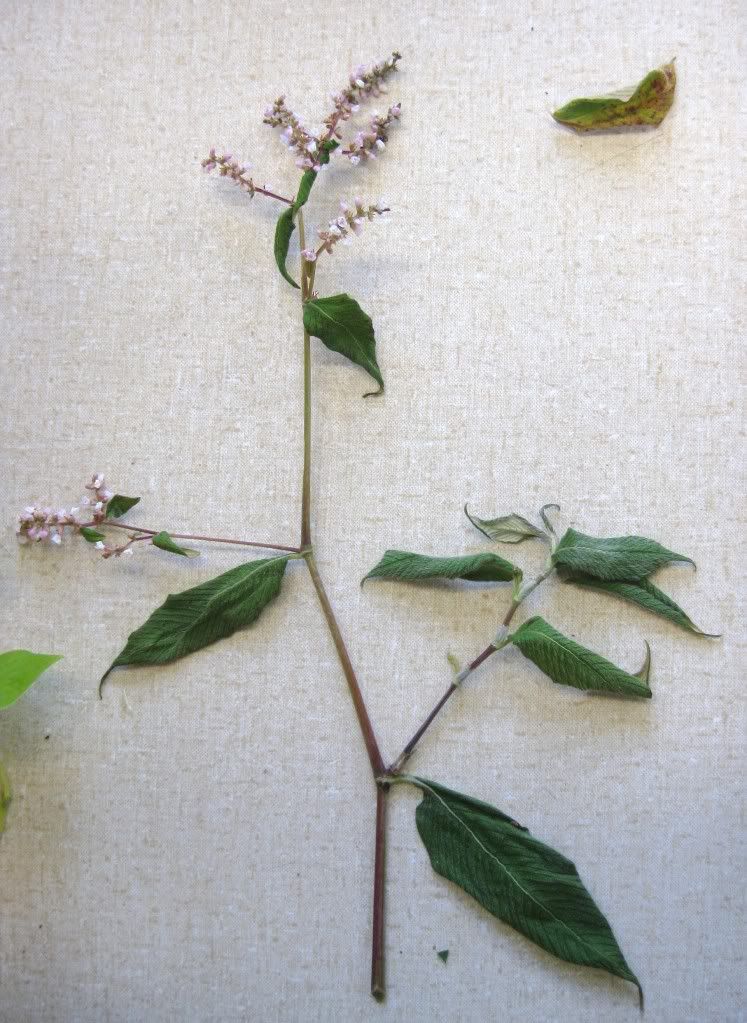

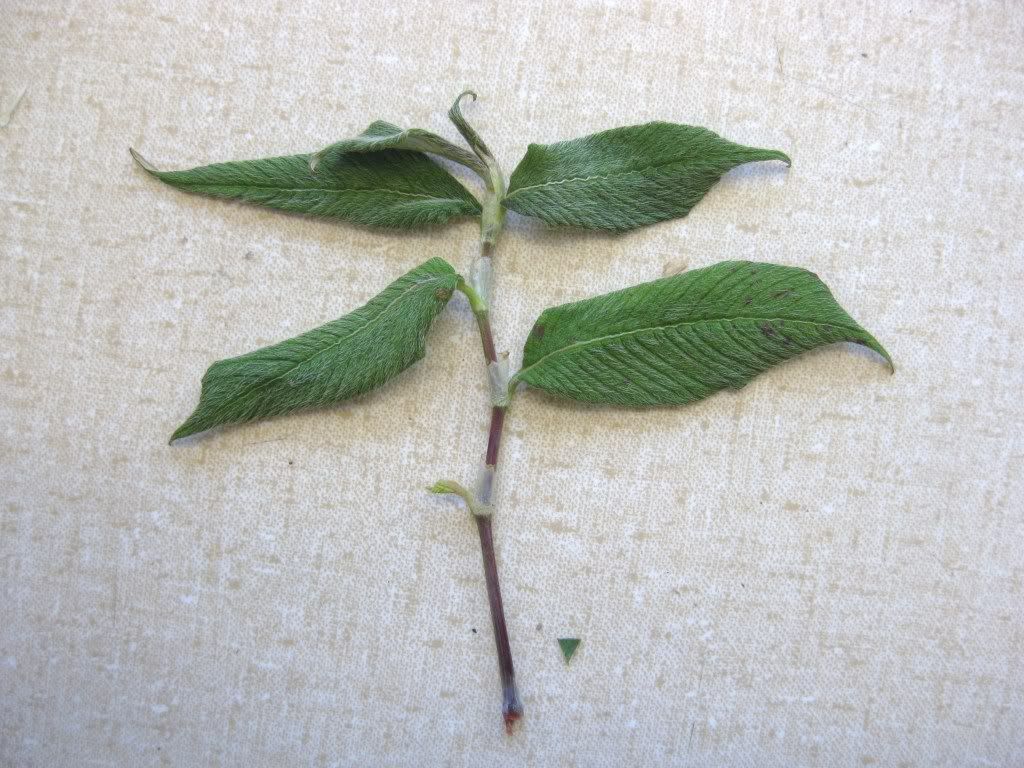
A branch of a Polygonum or Fagopyrum sp. They have simple leaves that alternates (one on the left and the next on the right). Note the swollen nodes in this plant.
The white membranous wrappings around the nodes are the stipular sheaths.
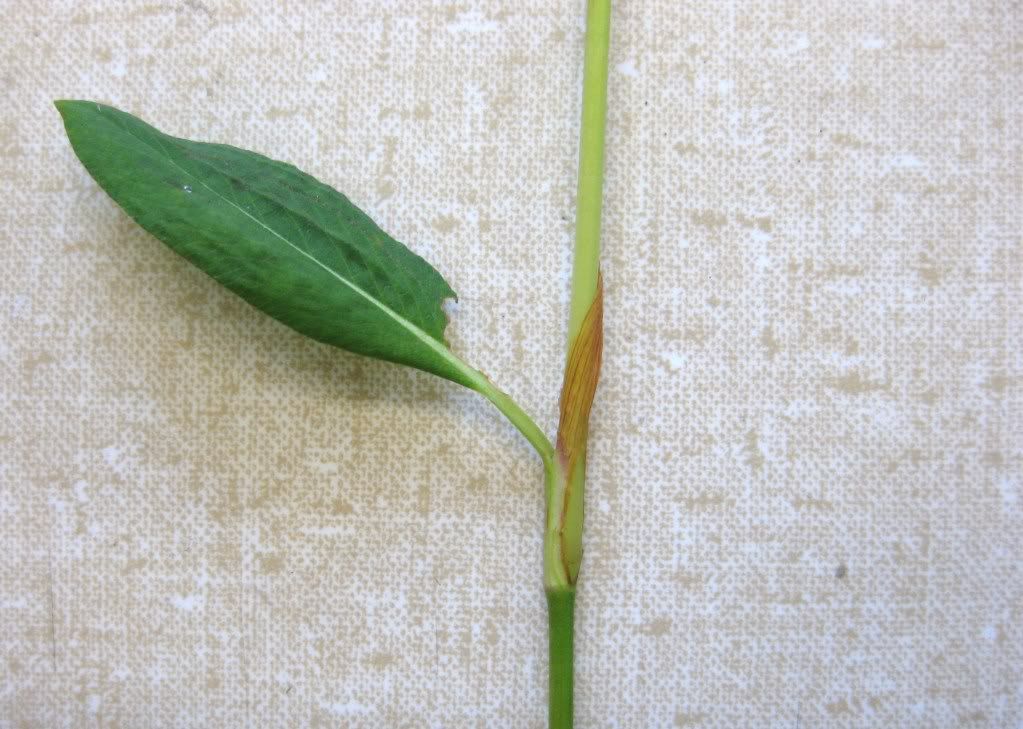
A close up of the stipular sheath at the base of the petiole.
This flower has a compound pistil with four stigma. Four stigma generally translates to a four carpel containing ovary.
A different flower, this one only has three carpels (therefore, three stigma).




.jpg)






No comments:
Post a Comment